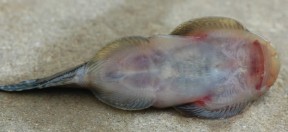
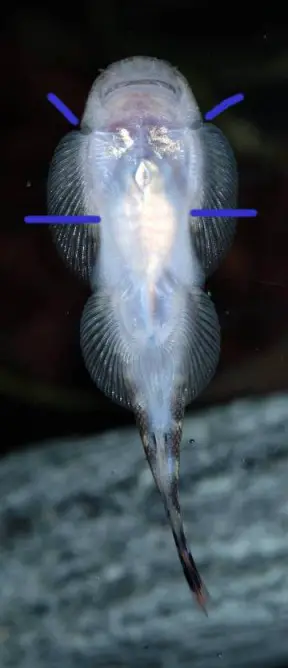
Gastromyzon aeroides
Etymology
Gastromyzon: from the Greek gaster, meaning ‘stomach’ and myzo, meaning ‘to suckle’.
Classification
Order: Cypriniformes Family: Gastromyzontidae
Distribution
Endemic to northern Borneo where it’s been recorded from the Petagas, Padas and Mengalong River drainages in western Sabah Province (Malaysia) and the Temburong River basin, Temburong District, Brunei Darussalam.
Type locality is ‘Sungai Malamus, about 9 kilometers into track, tributary to Mengalong River, 4°59.120’N, 115°37.581’E, Siptang, Mengalong River basin, Sabah, elevation 50 meters’.
Populations from Brunei and Sabah exhibit some differences, most notably in the number of lateral line scales (Brunei, 47-49; Sabah, 56-65) but are currently considered conspecific.
All members of the genus are endemic to Borneo with over half restricted to just a single river basin or sub-basin.
Habitat
Gastromyzon spp. are obligate dwellers of swift, shallow streams containing clear, oxygen-saturated water and have been recorded from sea level to 1350 m amsl throughout hill regions of Borneo.
They typically inhabit riffles and runs and are often found above or below cascades and waterfalls.
Substrates are generally composed of gravel, rocks, boulders or bedrock carpeted with a rich biofilm formed by algae and other micro-organisms.
Aquatic plants are uncommon and while riparian vegetation may be present these loaches tend to be most abundant in partially or fully-shaded zones.
Field observations have revealed that individuals typically position themselves facing into the flow, either along the sides, behind or under rocks, their specialised morphology (see ‘Notes’) allowing them to forage and maintain a particular spot without being swept away.
In nature G. aeroides occurs alongside Gastromyzon extrorsus (Petagas River), G. introrsus, G. lepidogaster (Padas River), G. borneensis, G. lepidogaster (Mengalong River), G. cranbrooki, G. lepidogaster, G. punctulatus, G. venustum and Neogastromyzon brunei (Temburong River).
At one high gradient locality in the Kiminis River (Petagas basin) the habitat was around 1.5 meters deep and 15 metres wide, but the fish were collected from a riffle about 30 cm in depth.
On 02 June 2009 at 10:30 am water temperature was 26.5 ºC, pH 7.6 pH, conductivity 140 µS/cm, and total dissolved solids 70 mg/l, while on 07 June 2009 at 15:00 pm water temperature was 28 ºC, pH 8.1, conductivity 60 µS/cm, and total dissolved solids 30 mg/l.
Maximum Standard Length
40 – 46 mm.
Aquarium SizeTop ↑
An aquarium with base dimensions of 60 ∗ 30 cm or equivalent is large enough to house a group.
Maintenance
Most importantly the water must be clean and well-oxygenated so we suggest the use of an over-sized filter as a minimum requirement.
Turnover should ideally be 10-15 times per hour so additional powerheads, airstones, etc. should also be employed as necessary.
Base substrate can either be of gravel, sand or a mixture of both to which should be added a layer of water-worn rocks and pebbles of varying sizes.
Aged driftwood can also be used but avoid new pieces since these usually leach tannins that discolour the water and reduce the effectiveness of artificial lighting, an unwanted side-effect since the latter should be strong to promote the growth of algae and associated microorganisms.
Exposed filter sponges will also be grazed, and some enthusiasts maintain an open filter in the tank specifically to provide an additional food source.
Although rarely a feature of the natural habitat aquatic plants can be used with adaptable genera such as Microsorum, Crinum and Anubias spp. likely to fare best. The latter are particularly useful as their leaves tend to attract algal growth and provide additional cover.
Since it needs stable water conditions and feeds on biofilm this species should never be added to a biologically immature set-up, and a tightly-fitting cover is necessary since it can literally climb glass.
While regular partial water changes are essential aufwuchs can be allowed to grow on all surfaces except perhaps the viewing pane.
Water Conditions
Temperature: For general care 20 – 24 °C is recommended but it can withstand warmer conditions provided dissolved oxygen levels are maintained. At the locality pictured above water temperature was 85.1°F/29.5°C in June 2009.
pH: 6.0 – 7.5
Hardness: 36 – 215 ppm
Diet
Much of the natural diet is likely to be composed of benthic algae plus associated micro-organisms which are rasped from solid surfaces.
In captivity it will accept good-quality dried foods and meatier items like live or frozen bloodworm but may suffer internal problems if the diet contains excessive protein.
Home-made foods using a mixture of natural ingredients bound with gelatin are very useful since they can be tailored to contain a high proportion of fresh vegetables, Spirulina and similar ingredients.
For long-term success it’s best to provide a mature aquarium with a plentiful supply of algae-covered rocks and other surfaces.
If unable to grow sufficient algae in the main tank or you have a community containing numerous herbivorous fishes which consume what’s available quickly it may be necessary to maintain a separate tank in which to grow algae on rocks and switch them with those in the main tank on a cyclical basis.
Such a ‘nursery‘ doesn’t have to be very large, requires only strong lighting and in sunny climates can be kept outdoors. Algal type is also important with diatoms and softer, green varieties preferred to tougher types such as rhodophytic ‘black brush’ algae.
Gastromyzontids are often seen on sale in an emaciated state which can be difficult to correct. A good dealer will have done something about this prior to sale but if you decide to take a chance with severely weakened specimens they’ll initially require a constant source of suitable foods in the absence of competitors if they’re to recover.
Behaviour and CompatibilityTop ↑
Very peaceful although its environmental requirements limit the selection of suitable tankmates somewhat, plus it should not be housed with any much larger, more aggressive, territorial or otherwise competitive fishes.
Potential options include small, pelagic cyprinids such as Tanichthys, Danio, and Rasbora, stream-dwelling gobies from the genera Rhinogobius, Sicyopterus, and Stiphodon, plus rheophilic catfishes like Glyptothorax, Akysis and Hara spp.
Some loaches from the families Nemacheilidae, Balitoridae and Gastromyzontidae are also suitable but others are not so be sure to research your choices thoroughly before purchase.
Gastromyzon spp. tend to exist in loose aggregations in nature so buy a group of 4 or more if you want to see their most interesting behaviour.
They’re territorial to an extent with some individuals appearing more protective of their space than others, often a prime feeding spot.
Sexual Dimorphism
Unreported but in congeners observed over time in aquaria adult females are noticeably heavier-bodied and often a little larger than males; the differences being more apparent when viewing the fish from above or below.
Reproduction
Has not been bred in aquaria and the only observations we know of for any member of the genus were made by German aquarist Philipp Dickmann and published in a hobbyist magazine during 2001.
He collected wild specimens of G. scitulus (identified as G. punctulatus at the time) and G. monticola, and attempted to spawn both using different methods.
Initially a pair of G. scitulus were placed in a 30 litre tank without substrate or filtration but heavily-aerated and containing some broken flower pots, boulders and floating plants for cover.
These were offered a rich diet with plenty of live and frozen mosquito larvae to bring them into breeding condition.
The temperature was then raised to 82.4°F/28°C over a period of 8 weeks and feeding increased; these conditions were maintained for 3 weeks during which the temperature unintentionally rose to 89.6°F/32°C.
After courtship behaviour was observed cool water changes were conducted to bring water temperature down to 77°F/25°C and the fish spawned during a period of low air pressure; at the point of climax their bodies are depicted to interlock away from the substrate.
At least 100 tiny (diameter <1 mm), sinking, non-adhesive eggs were observed and at this point the adults were removed.
The eggs began to hatch in around 3 days and the fry were initially photophobic and required an infusoria–type diet due to their small size (~3 mm SL). Apparently the plants in the tank began to rot resulting in a loss of water quality and after 3 weeks all the fry were dead.
More success was had with G. monticola, this time using a 160 litre tank with a coarse gravel substrate, some pieces of slate propped up against the rear pane, a clump of a Cryptocoryne sp. and a piece of driftwood.
Water temperature was maintained at 75.2°F/24°C and GH was 10-12°. This was again unfiltered but heavily-aerated with Ambastaia sidthimunki, Pangio sp. and a large population of the burrowing snail Melanoides tuberculata also in residence.
On this occasion small numbers of fry simply began to appear over time, and spawning was observed continuously over a period of 12 months.
NotesTop ↑
This species has probably not been seen in the aquarium trade yet but has been maintained by a few private collectors.
It can be separated from congeners by the following unique suite of characters: gill slit angular; presence of subopercular groove running to pectoral-fin origin; body colour, including dorsum, brown; head dorsum with fine, cream-coloured reticulate pattern; dorsal, caudal and anal fins coloured blue in life; presence of sublacrymal groove; snout appears rounded when viewed dorsally; absence of secondary rostrum; absence of postoral pouch; scales absent on belly; 47-65 scales in lateral line (specimens from Sabah: 56-65, Brunei: 47-49; pelvic-fin not overlapping anal-fin origin; adpressed dorsal fin not reaching level of anal-fin origin.
Gastromyzon spp. are placed into various species groups (putative assemblages of species which may or may not be monophyletic) for ease of reference, and G. aeroides is included in the G. punctulatus group which also contains G. punctulatus and G. katibasensis.
Members are defined by a combination of various characters of which the most useful for identification of live specimens include an angular gill slit, presence of a shalolow subopercular groove, body and head with cream spots (except G. aeroides which has brown/black spots) and brightly-coloured fins in live specimens.
The latter trait is particularly useful for identifying members of this group to species level since G. punctulatus has yellow dorsal, anal and caudal fins (the latter with red margins), G. katibasensis has red dorsal, anal and caudal fins, and G. aeroides blue dorsal, anal and caudal fins.
The body of G. aeroides is also plain vs. spotted in the other two species.
The current arrangement of species groups is as follows:
G. borneensis group: G. borneensis, G. monticola, G. ornaticauda, G. cranbrooki, G. cornusaccus, G. extrorsus, G. introrsus, G. bario.
G. punctulatus group: G. aeroides, G. punctulatus, G. katibasensis.
G. fasciatus group: G. fasciatus, G. praestans.
G. contractus group: G. contractus, G. megalepis, G. umbrus.
G. ctenocephalus group: G. ctenocephalus, G. scitulus.
G. lepidogaster group: G. lepidogaster, G. psiloetron.
G. ridens group: G. ridens, G. crenastus, G. stellatus, G. zebrinus.
G. danumensis group: G. danumensis, G. aequabilis, G. ingeri.
G. pariclavis group: G. pariclavis, G. embalohensis, G. venustus, G. spectabilis, G. russulus, G. viriosus.
G. ocellatus group: G. ocellatus, G. farragus.
G. auronigrus group: G. auronigrus.
Gastromyzon spp. have specialised morphology adapted to life in fast-flowing water. The paired fins are orientated horizontally, head and body flattened, and pelvic fins fused together.
These features form a powerful sucking cup which allows the fish to cling tightly to solid surfaces. The ability to swim in open water is greatly reduced and they instead ‘crawl’ their way over and under rocks.
The family Gastromyzontidae is currently considered valid as per Kottelat (2012).
It contains a number of genera which had formerly been included in several families and subfamilies, most recently Balitoridae, of which the most well-known in the aquarium hobby include Beaufortia, Formosania, Gastromyzon, Pseudogastromyzon, Hypergastromyzon, Liniparhomaloptera, Sewellia, and Vanmanenia.
References
- Tan, H. H. and Z. H. Sulaiman, 2006 - Zootaxa 1117: 1-19
Three new species of Gastromyzon (Teleostei: Balitoridae) from the Temburong River basin, Brunei Darussalam, Borneo. - Endruweit, M. (ed), 2012 - World Wide Web electronic publication, www.aquariophil.org, accessed on 2012.05.17
Aquariophil - Inger, R. F. and P. K. Chin, 1961 - Copeia 1961(2): 166-176
The Bornean cyprinoid fishes of the genus Gastromyzon Günther. - Kottelat, M., 2012 - Raffles Bulletin of Zoology Supplement 26: 1-199
Conspectus cobitidum: an inventory of the loaches of the world (Teleostei: Cypriniformes: Cobitoidei). - Rachmatika, I., 1998 - Raffles Bulletin of Zoology 46(2): 651-659
Gastromyzon embalohensis, a new species of sucker loach (Teleostei: Balitoridae) from the Bentuang Karimun National Park, West Kalimantan, Indonesia. - Roberts, T. R., 1982 - Proceedings of the California Academy of Sciences (Series 4) 42(20): 497-524
The Bornean gastromyzontine fish genera Gastromyzon and Glaniopsis (Cypriniformes, Homalopteridae), with descriptions of new species. - Tan, H. H., 2006 - Natural History Publications (Borneo), Kota Kinabalu: 1-245
The Borneo suckers. Revision of the Torrent Loaches of Borneo (Balitoridae: Gastromyzon, Neogastromyzon). - Tan, H. H. and K. M. Martin-Smith, 1998 - Raffles Bulletin of Zoology 46(2): 361-371
Two new species of Gastromyzon (Teleostei: Balitoridae) from the Kuamut headwaters, Kinabatangan basin, Sabah, Malaysia.